This article was originally published on Kevin-Indig.com.
Until 5 years ago, nobody in SEO cared about User Intent. Then everything changed, and it became the prerequisite for SEO. Without fulfilling the right user intent, a page won’t rank. What happened? Hummingbird (2013) and RankBrain (2015)!
Now, if you’re not completely new to SEO you knew this before. What has been a big challenge, however, is to apply this concept at scale. It’s simple to look at a query, understand the user intent, look at what’s ranking and say, “that fits” or “that doesn’t fit”. What’s not simple is having a spreadsheet with thousands of keywords and knowing which ones serve which user intent.
In this article, I show you how to solve this issue by scaling up user intent identification. We’ll start with updating our understanding of user intent, then cover the role of SERP* features and finally see how to map user intent to the buyer’s journey. (*Search Engine Results Page)
What is user intent?
“User intent” is the goal a user is trying to achieve when searching online. Old school SEO distinguished between “transactional”, “navigational”, and “informational” user intent. People either want to buy, visit a specific page or find out more about a topic.
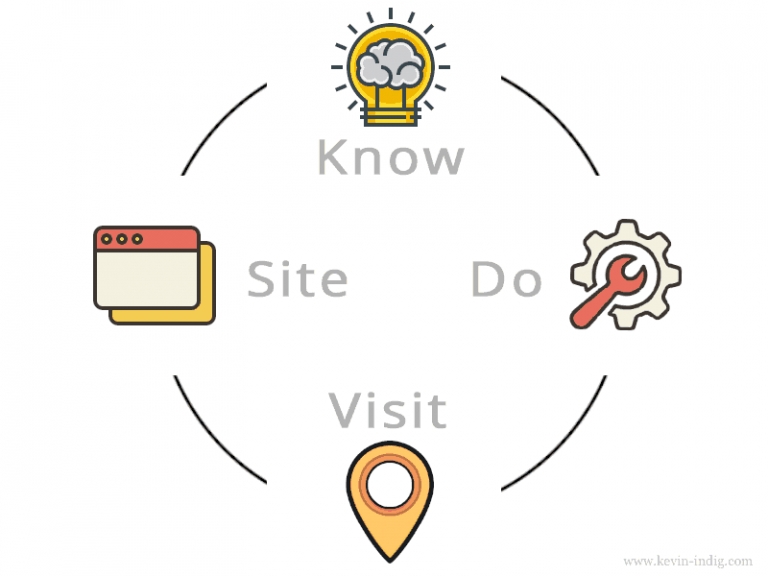
That hasn’t changed dramatically, but in the 2017 version of its quality rater guidelines, Google distinguishes between four intents:
- Know
- Do
- Website
- VISIT-IN-PERSON
(source: Google Quality Rater guidelines 2017[2])
From the four, “Website Queries” represent the classic navigational intent. However, for the other three intents, Google suggests an even finer segmentation.
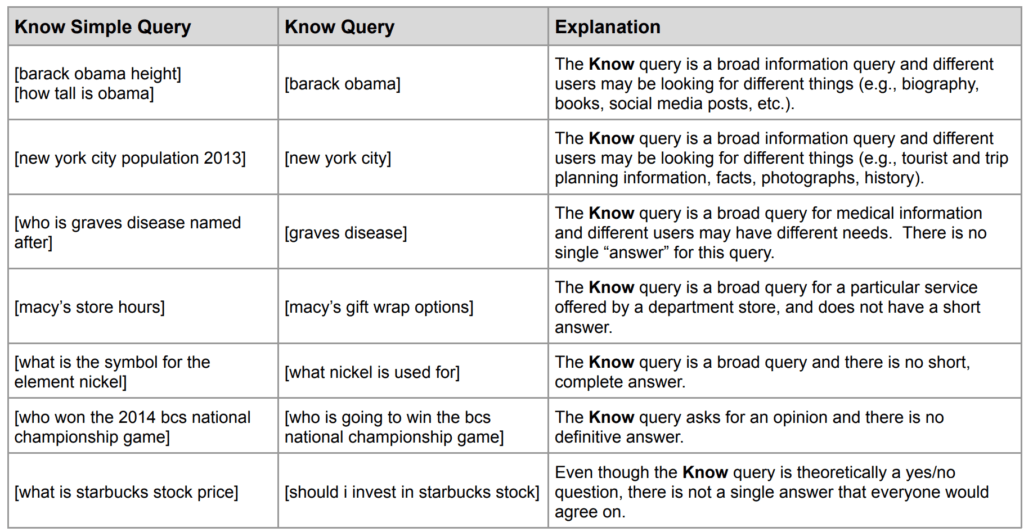
Know and Know Simple Queries
There are “Know” and “Know Simple” Queries, similar to informational queries.
Know Simple Queries seek for a very short answer to a simple question, for example, “Who is the president of the United States?”, “How many grams is a pound?”, or “When was the Second World War?”. They don’t have to come with a question modifier:
“President of the us” yields the same results as “Who is the president of the United States?”. Both share the same user intent.
Google defines “Know Queries” as:
- Broad, complex, and/or indepth informational queries that do not have a short answer
- Ambiguous or unclear informational queries
- Informational queries on controversial topics
- Informational queries with no definitive “right answer”
- Queries where different users may want different types of information or different sources of information
(source: Google Quality Rater guidelines 2017[2])
Know Queries cannot be answered in a simple way and instead needs more context. The user intent here can vary quite a bit. Say you search for “graves disease”: do you want to know what it is, how to treat it or how many people get it every year?
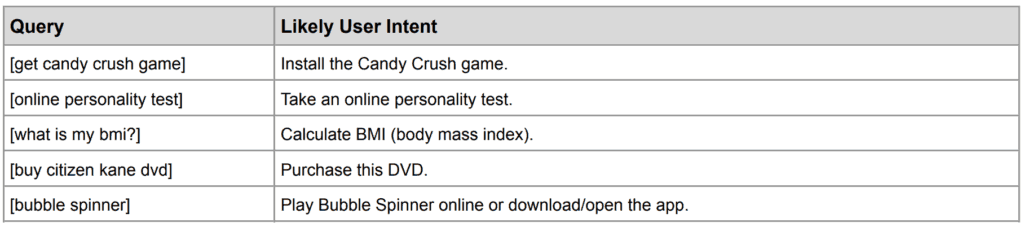
Do and Device Action Queries
About “Do Queries”, Google states that “the goal or activity may be to download, to buy, to obtain, to be entertained by, or to interact with a website or app.” They are the equivalent to the old notion of the navigational user intent.
(source: Google Quality Rater guidelines 2017[2])
It’s interesting to see that “online personality test” is a “Do Query”, even though it doesn’t contain an imperative, e.g. “take”. The same accounts for “Bubble Spinner”. My personal 0.02$ is that Google understands what people want here due to measuring user behavior in the SERPs (clicks) and adjusting the distance between the two word vectors (see box below), namely “take online personality test” and “online personality test”.
If that doesn’t ring a bell, here’s what I wrote about Word2Vec and word vectors in “How to rock SEO in a machine learning world”:
Again, Google differs between “Do Queries” and “Device Action Queries”. The latter is reserved for users who ask their phone to do something, e.g. by using “ok Google” or “Hey Siri”.
To stress the importance of voice search in the future once again, here’s what the Google Quality Rater guidelines say in the paragraph about Action Device Queries: “It’s very important for mobile phones to accommodate Device Action queries, and we have a high standard for rating these results.” 🤔
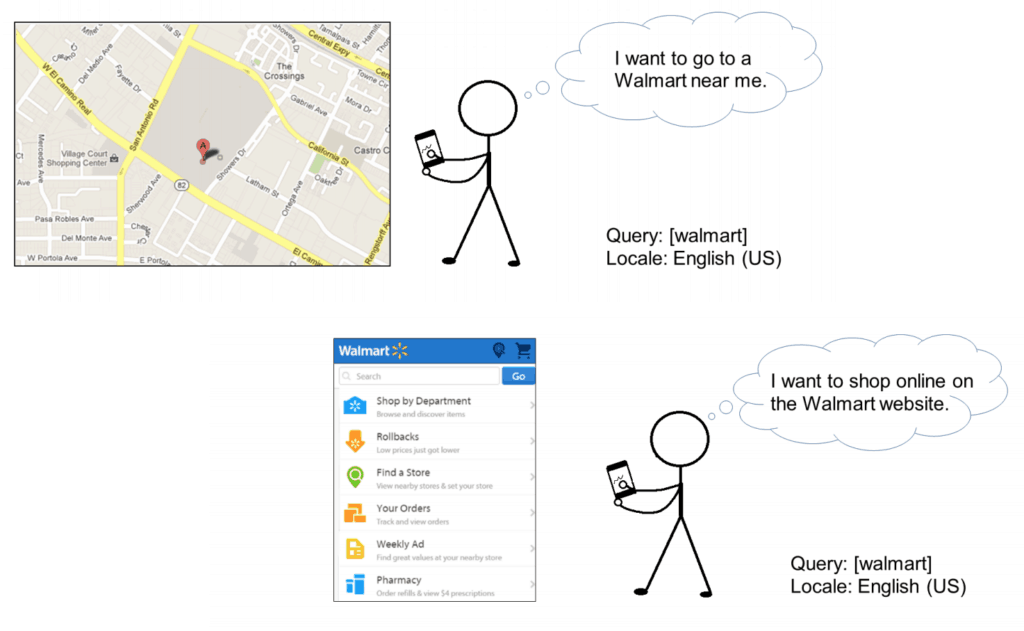
Visit-in-person Queries
(source: Google Quality Rater guidelines 2017[2])
So, to summarize, Google sees six user intents:
- Know and Know Simple
- Do and Device Action
- Visit-in-person
- Website
I personally think that Know and Know Simple Queries need an even finer segmentation, for two reasons.
First, I’ve seen the behavior of seeking inspiration on the internet for quite some time. Those could be Know Queries (“flower tattoos”) or Know Simple Queries (“what are nice cars”). Sites like Pinterest fulfill that intent very well, which is why the site ranks well for many brand and generic queries.
In “How to rock SEO in a machine learning world”,
I wrote: Pinterest competes with online retailers now because more transactional keywords also have an inspirational user intent (assumption). It used to be that people either wanted to learn or to buy online but nowadays people are skimming the internet to get inspired and find new things. It’s online window shopping.
So, maybe we should consider tutorials and inspiration as additional segments of Know and Know Simple Queries.
Now, that we have a clear understanding of user intent, we want to know how to map it to keywords. The key to that is SERP features.
(If you don’t care about the evolution of user intent, i.e. how it comes that it’s suddenly an important factor in SEO and why it changes, feel free to skip this section.)
The evolution and adoption of user intent
- New devices (smartphones, voice devices)
- Progression of search engines (better understanding of queries, better results)
- New possibilities in web development (JavaScript, widgets, formats, products)
Search on smartphones is not very different compared to desktop but the expectations are. Pages on mobile have to be fast, deliver the core value (content or product) quickly, and be user-friendly. People might have different expectations, such as a summary of the content to make it digestible on a mobile device.
Search, most notably Google, has undergone a rapid transformation in the past couple of years. The way search results look in 2018 vs. 2013 vs. 2008 is vastly different. The interface change also impacts user behavior.
One example is booking flights, which is now possible right in the Google search results (end-to-end) or checking the weather.
Another part of the evolution is Google’s advancing understanding of what the user actually wants (due to Rankbrain and Hummingbird). It takes for example into account what a user has searched for before, what device she’s searching on, and how she phrases her search (query). All this and more allows Rankbrain to serve specific results that are so good that people get used that and change the way they search.
Web technologies are the third major driver of changing searcher behavior. Websites have become interactive through JavaScript and new formats have evolved (Pinterest). Once users get a taste of a new technology that works well, they’re quick to expect it to appear everywhere. Think of Pinterest and the effect it had on how people browse (Zillow Digs, Houzz, Ikea).
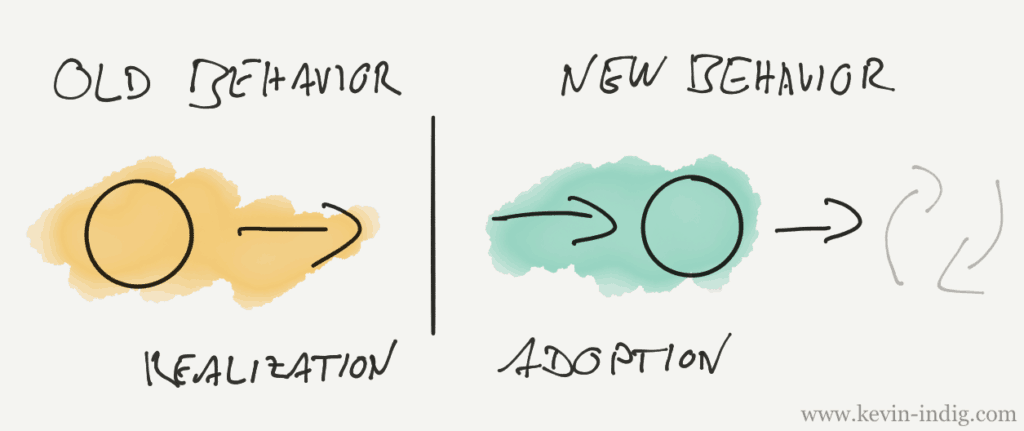
It always takes a bit of time between the rollout of a new feature (in search) and the user realizing that something new is now possible.
Reverse engineering user intent from SERP features
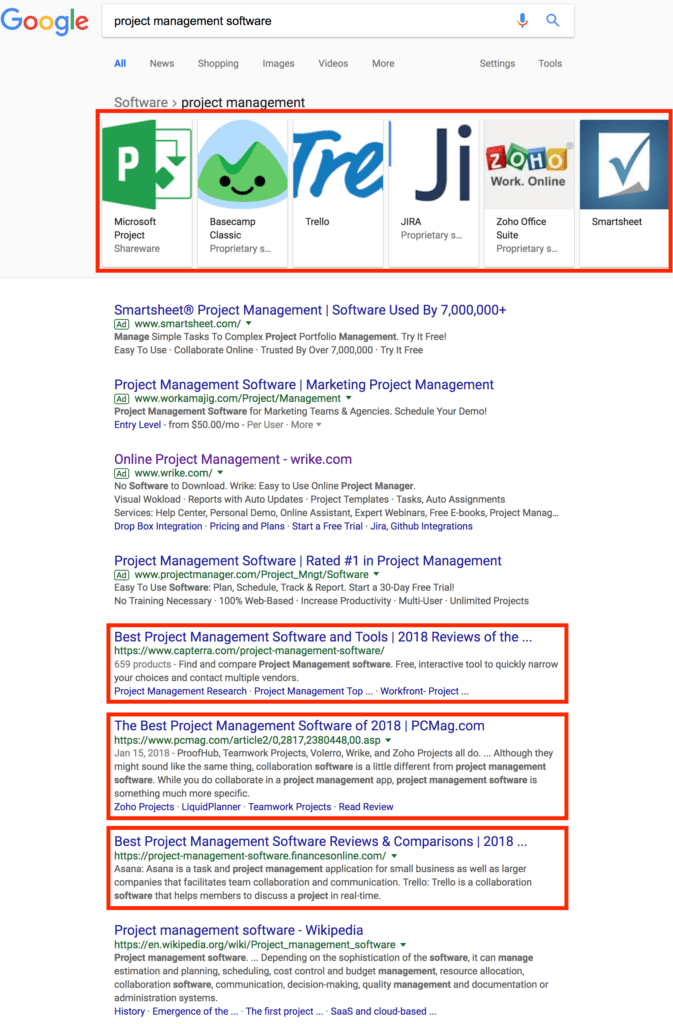
Imagine the keyword was “project management software” and we didn’t know anything about it. We would start by googling “project management software” and see what results rank on top.
When you look at the screenshot, it quickly becomes apparent that people who use the search query “project management software” seem to want to compare all solutions against each other.
The indicators are the Google Carousel on top of the SERP showing different project management software applications and the rankings pages (with meta-titles containing “best project management software”).
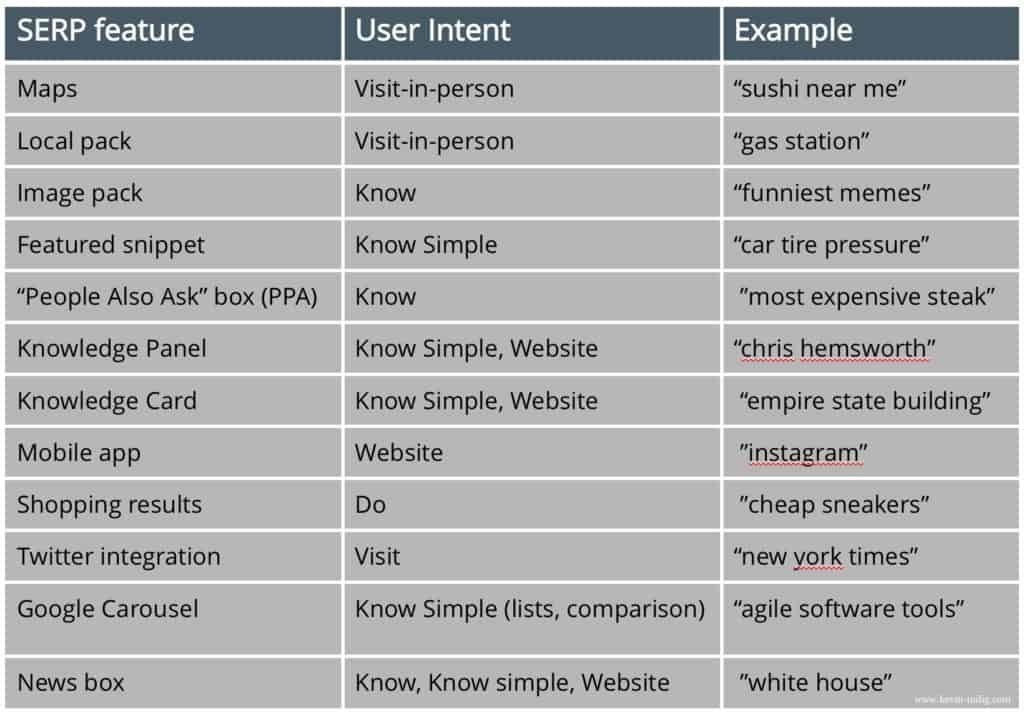
This is how we would do it manually for a single keyword. Since Google doesn’t rank pages that don’t satisfy user intent at least to a degree, the SERPs help us understand the user intent Google “sees” for a query. On top of the search results, Google displays certain features only for specific user intents. Have a look at this table, in which I mapped SERP features to user intents:
Note that some integrations are shown for several intents. The reason is that short-head queries allow for only so much understanding of the intent.
The role of long-tail vs. short-head for user intent
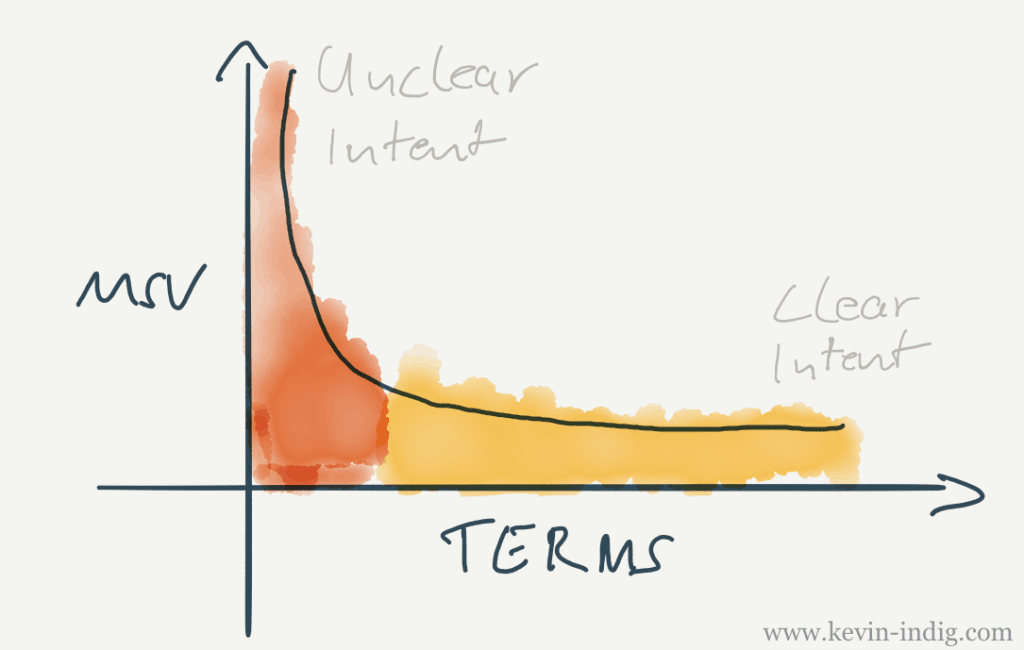
Long-tail queries provide more user intent that short-head queries. The longer the query, the more information it gives away.
The (negative) correlation between monthly search volume (MSV) and the number of terms also translates into user intent. It becomes clearer with more words in the search query but the search volume also gets smaller.
How to map user intent to keywords at scale
Now that we know we can identify user intent from looking at SERP features, let’s look at scaling it up. It’s easy to do keyword by keyword but what if you’re facing a spreadsheet with thousands of keywords?
That’s when tools come into play!
I found suitable functionalities in AHREFs and Searchmetrics. If you know other tools with similar or the same feature, please let me know.
Using Searchmetrics to scale user intent identification
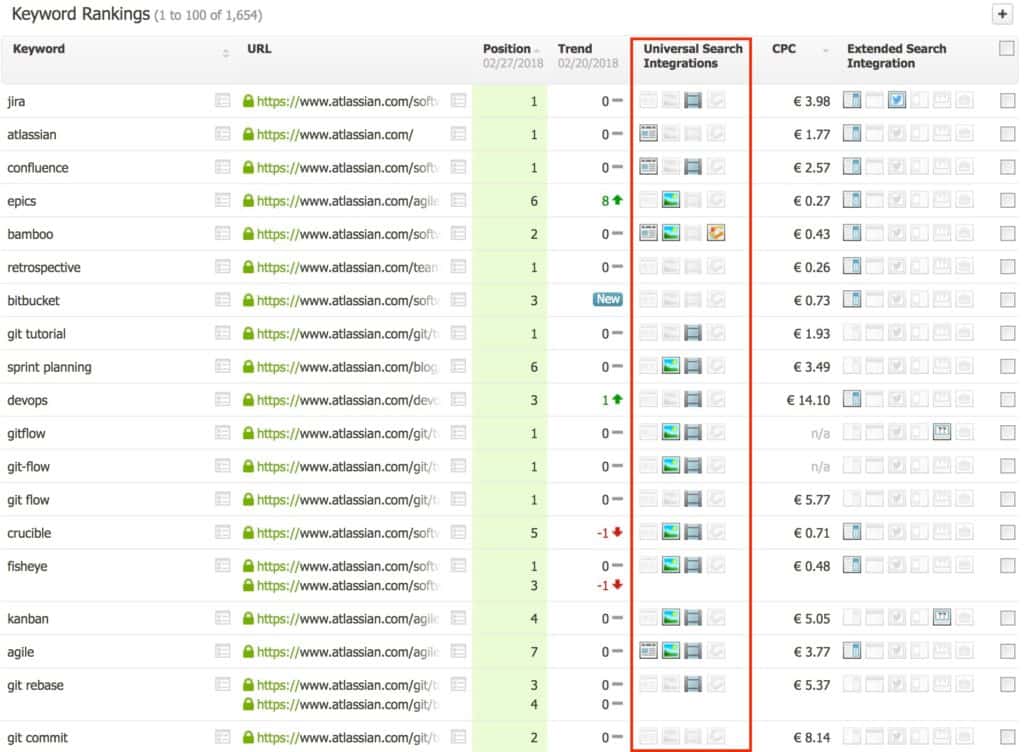
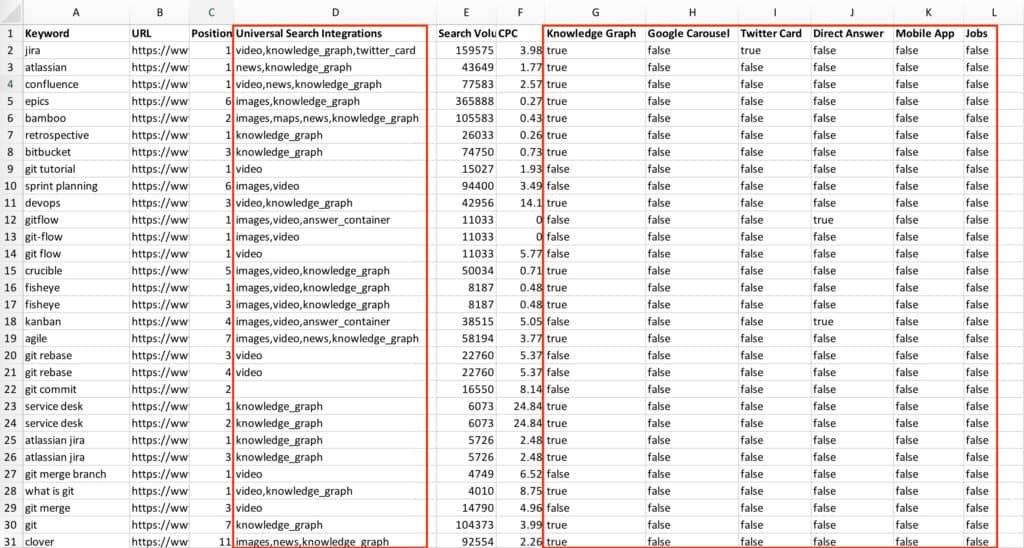
Searchmetrics allows you to define your own keywords in the project management section. Once you set them up, it gives you “universal search integrations” and “extended search integration”.
Example
So, you could filter after Featured Snippets (Searchmetrics names them “direct answers”), which, as outlined above, show up for Know Simple Queries.
If that was your keyword set, you now need to figure out how to rank for Featured Snippets and adjust the content on the pages you want to rank for these queries.
In order to rank for Featured Snippets, you should rank on position 1-5, include the Know Simple query in an h-tag, and provide the answer in a paragraph with 55-60 characters or a bulleted list. [3][4]Hubspot suggests that the shorter the query the more likely it will pull the featured snippet from a paragraph, rather than a list:
“For shorter, less question-orientated keywords that display a Featured Snippet (e.g. “Inbound Sales”), it’s much more likely that Google will pull through a paragraph of text as opposed to a step-by-step. Page structure is incredibly important here.” [4]
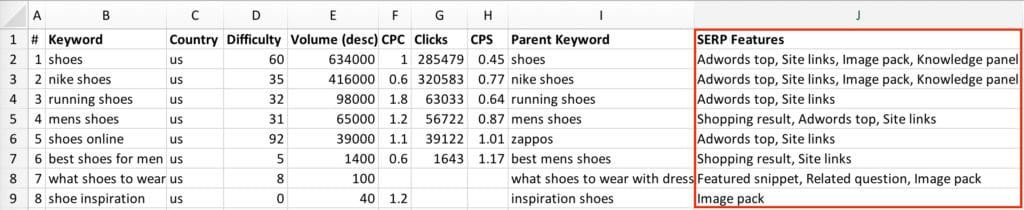
Using AHREFs to scale user intent identification
AHREFs allows you to analyze keywords in “Keywords Explorer” feature without having to set them up first. That makes it very comfortable to analyze competitors.
The next step is to tag your keywords in the SEO tool of your desire with the user intent you identified for them. That allows you to track whether you’re doing a good job in meeting them and if they still fit the SERP features we mapped them to.
Mapping user intent to the buyer’s journey
This last step is optional. You can also just take the matched queries from above and fit them into your strategy.
The buyer’s journey is a map of every step a user takes from having a need to buying again.
By mapping the queries and user intent to it you get a blueprint for your SEO content strategy.
Buyer Journeys can be very big and involved many (hundreds of) steps. Organic Search has multiple touch points with it and is sometimes part of each step.
Knowing the user intent and relevant queries for every stage is helps your company to be present along the whole buyer’s journey to ensure the customer buys from you.
On top of that, it’s a document that’s valuable for your whole organization, not just SEO.
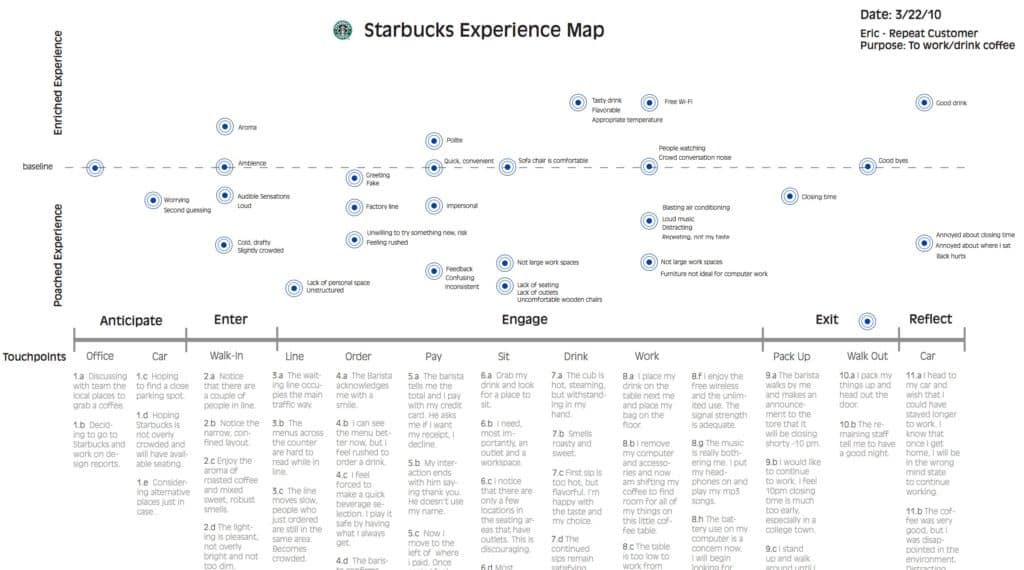
Starbucks’ buyer journey [6]
The high-level steps of a buyer journey are:
- Problem recognition
- Research
- Comparison
- Decision
- Post-sales
You can combine these five steps with the six user intents Google provides, and then group all of your search queries under each step. Let’s play this through for the example of buying razor blades online:
There are a couple of things to point out for this model:
First, SEO cannot technically “create” demand. But the user could realize her/his problem in the research of something else. We call this “Serendipity”: the idea of finding (out) something while searching for something else. This is the only way SEO can make people aware of a problem they might have.
Second, in every stage, the user could have a navigational user-intent if she/he feels strongly about a destination. It could be that a user trusts a site so much that she/he starts her research on it. For reviews that could be Amazon, for research that could be Quora or WikiHow. I left that part out because it’s too hypothetical and would be the same in each step.
Third, there are different buyer journeys for each persona and different search queries in each stage of the buyer’s journey. Women shave, too, for example. However, since their needs are different, they would use different search queries. If you’re not aware of that you could miss a huge chunk of the market.
When you start out, focus 1-2 personas and the three most important buyer journeys. 3-4 buyer personas seem to carry over 90% of companies’ business. [1]
Once you have this mapped out, you can do a gap analysis to understand where you’re lacking content or where it’s underperforming. With this document at hand, you don’t only know what (landing) pages you need but also how to design them. Looking back at the example above, “How to look more put together” could be targeted by a blog post that covers the step by step process. while “Shave or trim?” could be a landing page. For “[brand x] vs. [brand y]” you definitely want to create its own page type
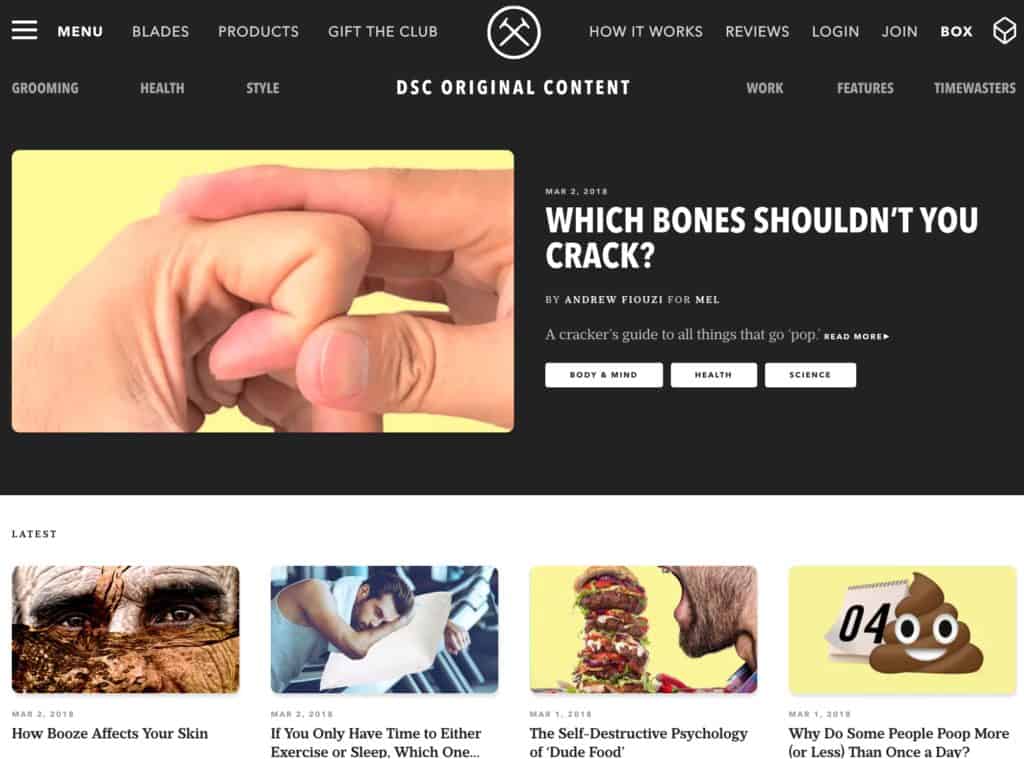
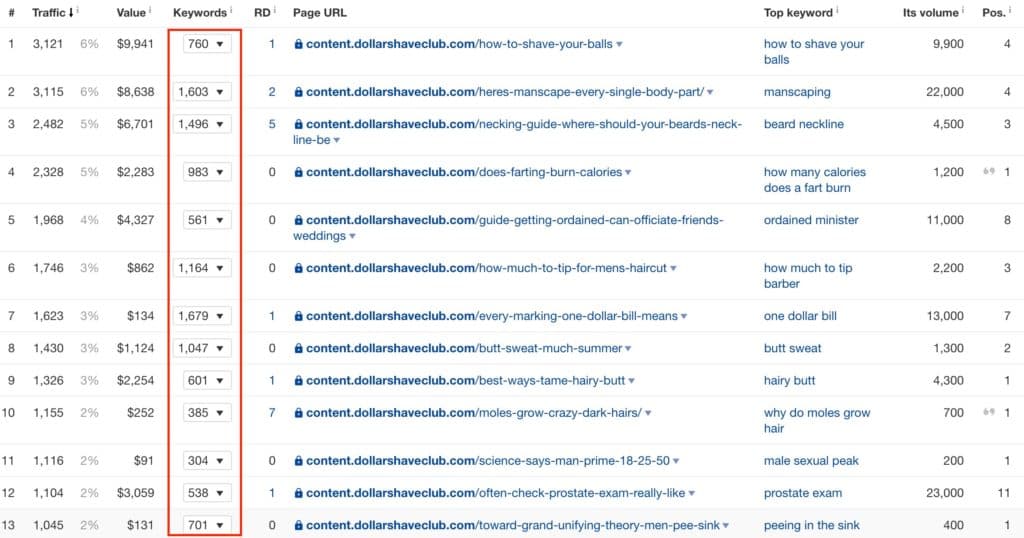
To show an example from the wild, look at Dollar Shave Club’s original content section. It’s a pure awareness play: DSC doesn’t promote products in this section. It’s just helpful content that addresses specific needs of men.
(content.dollarshaveclub.com)
They are wildly successful with this format and each article ranks for many keywords. (I don’t understand why they put the content on a subdomain, though ¯\_(ツ)_/¯ )
tl;dr – How to identify user intent at scale
The idea I want to promote is to look at Google’s SERP features (e.g. Featured Snippets) to identify user intent.
To scale this concept up:
- Take your keyword set and throw it into Searchmetrics (Project Suite > Organic Rankings) or AHREFs (Keywords Explorer).
- Export your keyword list to get the SERP features.
- User the table above (section “Reverse engineering user intent from SERP features”) to know which user intent is represented by which SERP feature.
- Tag your keywords with the user intent and re-upload them into your keyword tool.
- Optionally, you can map queries with user intent to your buyer’s journey.
Be aware that user intent can change over time. Just consider queries like “president of the united states” or “apple”. It’s a dynamic concept, so make sure to recalibrate on a regular basis.
References
- https://www.businessesgrow.com/2014/02/12/31-business-building-benefits-buyer-personas/
- http://static.googleusercontent.com/media/www.google.com/en//insidesearch/howsearchworks/assets/searchqualityevaluatorguidelines.pdf
- https://www.semrush.com/blog/large-scale-study-how-to-rank-for-featured-snippets-in-2018/
- https://ahrefs.com/blog/featured-snippets-study/
- https://moz.com/blog/what-we-learned-analyzing-featured-snippets
- http://theoperationsblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/experiencemap1.pdf
- http://www.evolvingseo.com/2018/03/08/090-aj-kohn/